Introduction
Chemotherapy drugs, vital in cancer treatment, are not without risks for healthcare professionals, particularly nurses. Their handling poses occupational hazards due to the drugs’ potent and toxic nature. Understanding these risks and the protective measures provided by Closed System Drug-Transfer Devices (CSTDs), especially EQUASHIELD’s CSTD, is crucial for healthcare workers’ safety.
The Occupational Risks of Handling Chemotherapy Drugs
According to the CDC, healthcare workers, particularly nurses and pharmacists, face significant risks when handling chemotherapy drugs. The NIOSH (National Institute for Occupational Safety & Health) article, “Hazardous Drug Exposure in Healthcare,” states that these risks can lead to “acute and chronic health effects such as skin rashes and reproductive issues.”
This includes “infertility, spontaneous abortions, and congenital malformations” as well as an increased risk of “leukemia and other cancers.” Exposure over time is associated with birth defects and miscarriages.

Key Exposure Points For Health Professionals
Exposures occur through the compounding process and frequent handling of these drugs during administration. Healthcare workers, including nurses and pharmacists, who are in direct contact with these potent and toxic substances, are seen as the more vulnerable groups.
According to OSHA, exposure to hazardous drugs during preparation and administration poses significant health risks, including cancer, organ toxicity, and reproductive issues. Occupational hazards are increased in the preparation phase while complying with the very low level of pharmacological compounding compared to the administration phase. The levels of risk are pretty high, and they result from processes that expose workers to substances that have the potential to cause harm.
Therefore having proper knowledge of the harmful agents associated with this process and the safeguarding measures, such as the EQUASHIELD’s Closed System Drug Transfer Devices (CSTD), would go a long way in enhancing the work-related health and safety of the healthcare workers.
Routes of Exposure
Health workers can inhale chemotherapy drug particles or vapors when preparing or giving treatment. OncoLink, a cancer resource in Pennsylvania, warns about these exposure risks. They state inhaling vapors is dangerous and can lead to other exposure through skin contact or needlestick accidents. Strict safety measures must be used to prevent these exposure risks.
Monitoring surface contamination of hazardous drugs is crucial, as evidenced by findings from a study conducted by the Canadian Journal of Hospital Pharmacy.
The study highlights that these hazardous drugs can settle on work surfaces and pose a risk of indirect transfer through contact, emphasizing the importance of regular environmental monitoring and rigorous cleaning protocols to safeguard healthcare workers from occupational exposure.
Threats on Healthcare Workers
A case study from the University of Michigan on the threats that affect cancer care workers found that nurses “handling hazardous drugs had twice the risk of reproductive problems.”
The lead study author, Christopher R. Friese elaborates, “This is an invisible threat.” He further examines, “Early on we could understand that a needle stick conveyed serious health risks… This is a subtle threat, but it’s a daily threat.”
The Role of EQUASHIELD’s CSTD in Protecting Healthcare Workers
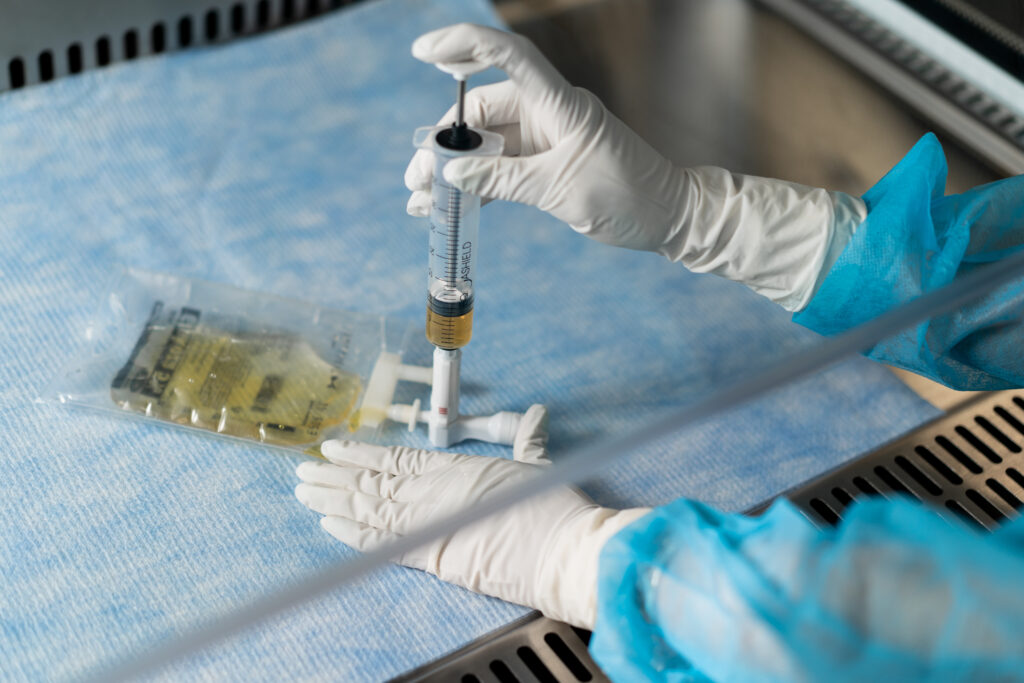
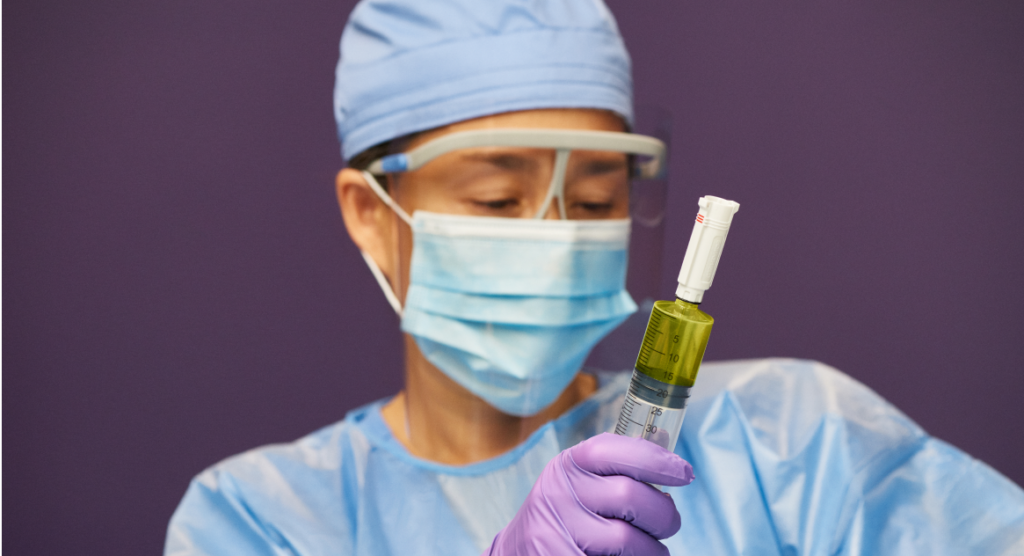
EQUASHIELD’s CSTD provides a crucial layer of protection against these occupational risks. By design, it mechanically prohibits the transfer of environmental contaminants into the system and the escape of hazardous drug or vapor concentrations outside the system, thus minimizing the risk of exposure during the compounding and administration of hazardous drugs.
The use of EQUASHIELD’s CSTD can “effectively eliminate spills and leakage during the compounding of gemcitabine” and antineoplastic drugs. According to the article “Maximizing Efficiency and Safety in Healthcare: Real Life Case Studies on Cost Savings with Closed System Drug Transfer Devices (CTSDs),” it can significantly reduce the risk of surface contamination and exposure. Therefore providing a safe working environment for anyone in the space.
Highlighting EQUASHIELD’s CSTD studies, the National Library of Medicine inscribes the effectiveness of “Reducing Leakage during Antineoplastic Drugs Compounding,” EQUASHIELD discovered that gemcitabine (GEM) was not detected in samples when using the EQUASHIELD® II system, indicating its effectiveness in preventing contamination.
Moreover, a significant reduction in detectable levels of antineoplastic drugs “in surface sampling wipes after the implementation of the EQUASHIELD’s CSTD.” Notably, the design of EQUASHIELD with a metal rod as a syringe plunger prevents contamination of the plunger itself, a common contamination site in other CSTDs.
Comparative Analysis with Other CSTDs
EQUASHIELD has been compared with other CSTDs in terms of containment of liquids and vapors – demonstrating its effectiveness in reducing operator exposure to hazardous drugs reinforces the critical role of CSTDs like EQUASHIELD in protecting healthcare workers.
When addressing the issue of hazardous drug exposure and the transfer of environmental contaminants, NIOSH employs a CSTD successfully. It creates “an airtight seal between drug vials, syringes, and IV bags.” This mechanical approach “prevents the release of harmful aerosols and vapors.” It greatly reduces risks from direct contact, skin exposure, and inhalation.
Conclusion
The occupational hazards of handling chemotherapy drugs are significant and can seriously impact healthcare workers’ health. Using CSTDs, especially EQUASHIELD’s CSTD, effectively reduces these risks by preventing drug leaks and surface contamination. Healthcare facilities must adopt such protective measures to ensure staff safety and well-being.