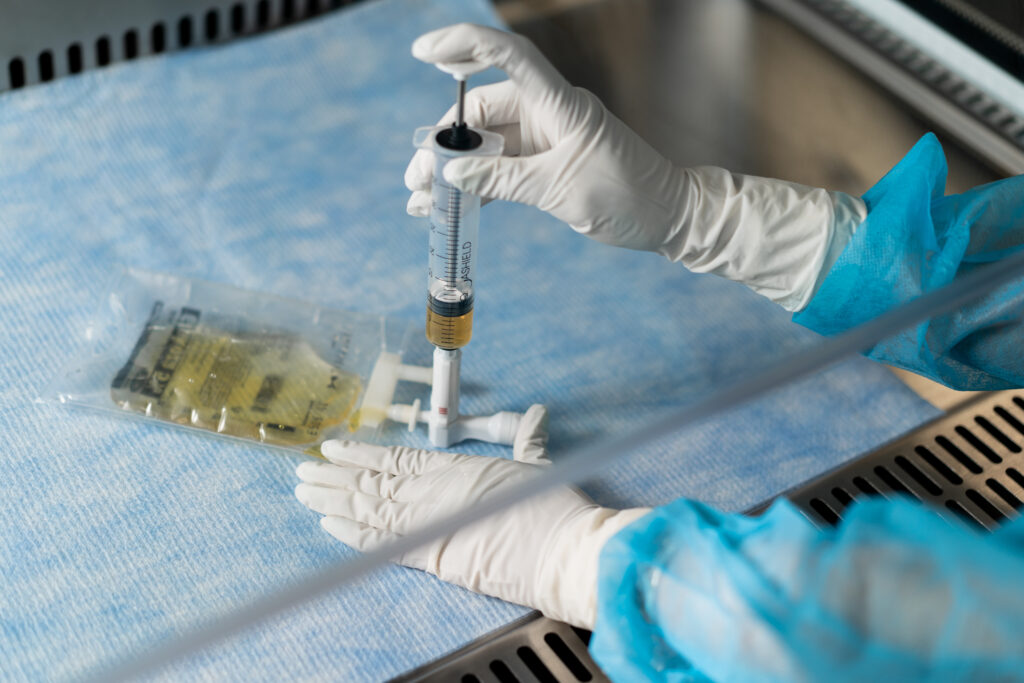
Closed System Transfer Devices (CSTDs) play a critical role in protecting the health of pharmacy staff during hazardous drug compounding. Each year, over 8 million healthcare professionals in the US and 12 million in Europe face the risk of exposure to hazardous drugs, a concern that has been extensively studied. (1)(2) CSTDs, with their advanced design, serve as powerful barriers, preventing exposure to dangerous drugs and reducing contamination. They also minimize waste and enhance the well-being of the staff working in hospitals and pharmacies.
In the following sections, we will explore the significant impact of CSTDs on the compounding process.
The Key Benefits of Using CSTDs in Pharmaceutical Compounding
A closed-system drug transfer device effectively minimizes contamination risks in healthcare settings.

Prioritizing Safety with Closed-System Transfer Devices
Closed System Transfer Devices (CSTDs) have become essential tools in drug compounding for both pharmacists and nurses, in order to address the issue of hazardous drug exposure. According to NIOSH, a CSTD mechanically prohibits the transfer of environmental contaminants into the system and the escape of hazardous drug or vapour concentrations outside the system.(3) By creating an airtight connection between drug vials, syringes, and IV bags, they successfully prevent the release of harmful aerosols and vapours, significantly reducing the risks associated with direct contact, skin exposure, and inhalation. (4)
More Occupational Safety with CSTDs
CSTDs employ various technologies, each offering different levels of safety. Physical barriers establish a closed system, containing hazardous drugs, while air-cleaning technology filters out particles from the air. (5) This rigorous containment strategy provides a protective environment for healthcare staff, minimizing the potential long-term health risks associated with hazardous drugs.
Reducing Contamination Risks and Occupational Exposure to Chemotherapy Drugs
One standout benefit of a closed-system drug transfer device is the significant reduction in contamination hazards for healthcare workers. Research shows a substantial decrease in hazardous drug exposure when CSTDs are the preferred medical devices in use, with a contamination rate of 12.24% compared to 26.39% with standard isolators. (6) By adopting CSTDs, pharmacists, nurses, clinicians, and other staff can enhance safety measures, creating a safer and more secure healthcare setting.
Contamination Control in Chemotherapy Drug Compounding: CSTDs vs. open systems
In this section, we will compare CSTDs with their market alternatives. We will shed light on their distinctive features and provide guidance on the most suitable choice for various drug-compounding scenarios.

CSTD products
These devices maintain a sealed environment throughout the drug preparation process. Equipped with vial adapters and other components, CSTDs ensure that hazardous drugs are contained, protecting pharmacy staff. Particularly for dangerous drugs, CSTD performance is invaluable, effectively preventing the release of aerosols or vapours.
Open Systems
Open systems possess a degree of permeability due to their inherent lack of a complete seal. They are simpler and often more affordable, making them suitable for drugs with a lower contamination risk. However, their protective capabilities do not match those of CSTDs.
In conclusion, CSTDs offer enhanced protection, especially for hazardous drugs. The choice between CSTDs or alternative solutions should be based on the nature of the drug (hazardous vs non-dangerous), potential staff risks, and regulatory standards, always with a focus on safe and secure compounding. When compounding hazardous drugs one should always use CSTDs as the devices are the only ones able to ensure safety during the process.
The Mastery of Contamination Prevention
In addition to their numerous benefits, CSTDs excel at preventing contamination. Their design provides a dual defence mechanism: they prevent environmental contaminants from entering the system and ensure that hazardous drug particles and vapours are securely sealed within. This robust shield significantly reduces the danger of accidental contamination, setting CSTDs apart in terms of efficiency and protection for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
How do CSTDs prevent drug spills and leakage?

Furthermore, CSTDs offer impeccable protection against drug spills and leakage. They accomplish this through a foolproof mechanism that restricts the entry of environmental contaminants and securely contains hazardous drugs or vapours. Once activated and sealed, the CSTD system prevents any inadvertent entry or exit, including bacteria or particulate matter. This level of precision safeguards the compounding process from unintended breaches, highlighting the unparalleled capability of CSTDs in ensuring the integrity of drug handling.
The Financial Benefits of Transfer Devices with Closed Systems
In the world of healthcare, financial considerations are just as important as security. That’s why we’re taking a closer look at the economic advantages of CSTDs. This section explores how CSTDs save money and reduce waste, highlighting the long-term financial benefits of investing in these devices in the healthcare sector.

Using a Drug Transfer Device Enables Cost Savings through Waste Reduction
Using CSTDs offers significant cost savings by minimizing drug waste. By providing protection against microbial growth, the use of the vial can be extended, allowing for longer periods of use beyond the original expiration date. Studies show that implementing CSTDs reduces drug waste by an average of 72.5%. (7) This not only conserves valuable medications but also has a positive environmental impact by reducing the disposal of hazardous drugs.
Optimizing Drug Compounding with CSTDs
Efficiency studies have demonstrated that the closed systems extend the sterility of single-use vials, enabling the practice of vial sharing which significantly cuts down the volume of drugs thrown away after just one use. Remarkably, studies highlighted that CSTDs can preserve vial sterility for as much as seven days, with contamination rates remaining negligible up to 30 days, leading to considerable financial savings due to reduced drug wastage (8).
These devices not only ensure precision in medication measurement and dispensing, leaving minimal residue, but their design also prevents any medication leaks and drips, maximizing every drop. The controlled air pressure and accurate dosing provided by CSTDs also play a crucial role in averting the risks associated with overfilling or underfilling vials, which further trims down waste. Such efficiency has been shown to provide substantial economic benefits. Cost savings from integrating CSTDs into healthcare practices range from 7-15% on overall drug and device expenses. This can translate into annual savings of around £480,000 by recovering an average of 57% of unused drugs from vials, with Hungarian hospitals reporting noteworthy savings, particularly with costly parenteral biological agents (9). Collectively, CSTDs make a compelling case not only for their role in reducing drug waste but also for optimizing healthcare resources through their economic use.
Enhancing Results by Integrating CSTDs with DVO
Combining CSTDs with Drug Vial Optimization (DVO) techniques provides a comprehensive approach to protection and efficiency. While CSTDs ensure a secure drug-handling environment, DVO maximizes medication extraction from vials with minimal residue. This combination not only protects healthcare professionals but also offers long-term financial benefits, establishing a sustainable and cost-effective solution for patient care and financial health.
Factors that influence the vial savings when compounding hazardous drugs with CSTDs and DVOs
Calculating vial savings during the preparation of cytostatic drugs with CSTDs and Drug Vial Optimization (DVO) depends on multiple variables, such as the drug specifics, equipment, and compounding procedures. Key considerations include:
Drug concentration: Higher concentrations may yield more doses per vial, enhancing DVO savings.
Vial size: Bigger vials could result in more savings by optimizing usage.
Vial cost: Selecting vials should be cost-effective, balancing the price per millilitre with potential waste.
Shelf life: Consider the drug’s stability post-mixing to prevent waste from expiring drugs.
Compounding efficiency: Properly trained staff using CSTDs and DVO can minimize errors and waste.
Regulatory adherence: Comply with all regulations to ensure safe compounding practices.
Demand analysis: High demand for a drug could mean significant savings through vial optimization.
DVO efficiency: The efficacy of the DVO technology used affects the amount of extractable doses.
Drug properties: Consider the compounding impact of drug characteristics like viscosity and solubility.
Staff education: Skilled staff using CSTDs and DVO technology can maximize their well-being at the workplace while increasing cost savings.
Long-Term Cost Savings: CSTDs vs. Alternative Solutions
In addition to the economic and sterility benefits presented earlier, CSTDs address also the financial consequences of contamination in healthcare settings. Exposure to hazardous drugs poses risks to healthcare professionals and patients, resulting in significant financial strains. These strains include costs associated with potential medical expenses due to staff harm, and the management of contamination fallout. Using CSTDs in drug compounding provides a key solution for such issues and ensures financial profitability in the long term.
The Ripple Effect: The Costs and Consequences of Staff Exposure to Hazardous Drugs
Human errors in healthcare settings can have detrimental effects on staff, leading to a series of costly repercussions. Immediate expenses include medical treatment, testing for exposure to hazardous drugs, and time off work. Furthermore, staff illnesses can result in workforce shortages, requiring the need for temporary hires and additional expenses. These issues disrupt operations and drive up costs. Additionally, if patients are adversely affected, legal and compensation expenses may arise. Given these financial strains, it is crucial to implement preventive strategies to address the broad impact of staff exposure incidents. (10)
Mitigating Contamination Costs with CSTDs: A Proactive Approach
By using Closed-System Drug-Transfer Devices (CSTDs) to ensure a sealed environment during drug preparation and administration, the risk of staff contamination can be significantly reduced. This helps minimize immediate medical expenses related to exposure treatments, prevents operational disruptions, and eliminates the likelihood of legal and compensation claims. Implementing CSTDs demonstrates a proactive commitment to healthcare safety, protecting the well-being of healthcare professionals while also ensuring cost-effectiveness in operations.
Maximising Your CSTD Return on Investment by Investing in Staff Education
Investing in staff education for the proper use of Closed System Transfer Devices (CSTDs) is paramount in the healthcare sector, both for ensuring safety and enhancing financial outcomes. Effective training equips staff with the necessary skills to operate, maintain, and create efficient protocols for CSTDs, leading to fewer errors, reduced contamination risks, and improved chemotherapy administration. This not only advances patient care and satisfaction but also significantly increases return on investment (ROI) by minimizing costly mistakes such as drug spillage and avoiding needlestick injuries, which can cost between £10,000 to £620,000 alone, according to a report in Scotland. (11) Hence, comprehensive training is a strategic investment that yields long-term financial benefits by optimizing medication use and reducing healthcare risks. Equashield provides free training for all healthcare professionals interested in improving occupational safety and well-being in hospitals and pharmacy environments.
Choosing the Right CSTD: Factors to Consider
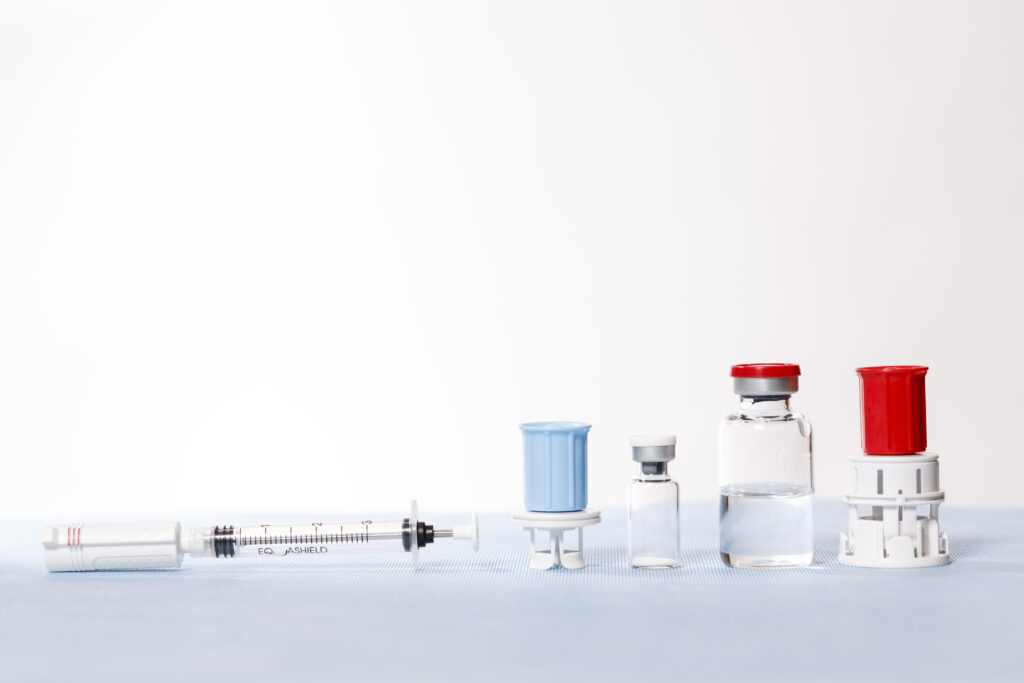
Selecting the appropriate CSTD is not as simple as choosing any other item. Comparing CSTDs in a real-world setting requires thorough education for all staff involved in testing. Here are the key aspects to consider when selecting a CSTD:
Safety: When it comes to handling hazardous drugs, the safety of healthcare personnel is the top priority. Utilizing a completely closed CSTD is crucial to provide the utmost level of protection against the risks linked to exposure and contamination.
Compatibility: Ensure the CSTD is compatible with all tubing and pump equipment used in your facility.
Effectiveness: Evaluate the device’s ability to prevent work environment contamination and exposure to high vapour concentrations when disconnecting IV tubing after infusion.
Ease of use: Choose a device that is user-friendly and does not require extensive training.
Cost: Consider the device’s total cost of ownership and its fit within your facility’s budget.
Reliability: Select a device with a proven track record of success and reliability. Those designed with the closed-back syringe tend to be the safest and show the highest CSTD performance.
Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Regulations and Protocols
Before integrating a Closed System Transfer Device (CSTD) into your healthcare facility, it is crucial to ensure it aligns seamlessly with your country’s existing protocols and regulations. Different regions may have specific guidelines for medication safe handling and increased risk exposure. Verify that the chosen CSTD meets the regulatory requirements and healthcare protocols in your area. This step is vital for maintaining compliance, enhancing patient safety, and streamlining your drug transfer processes.